Antibiotics, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
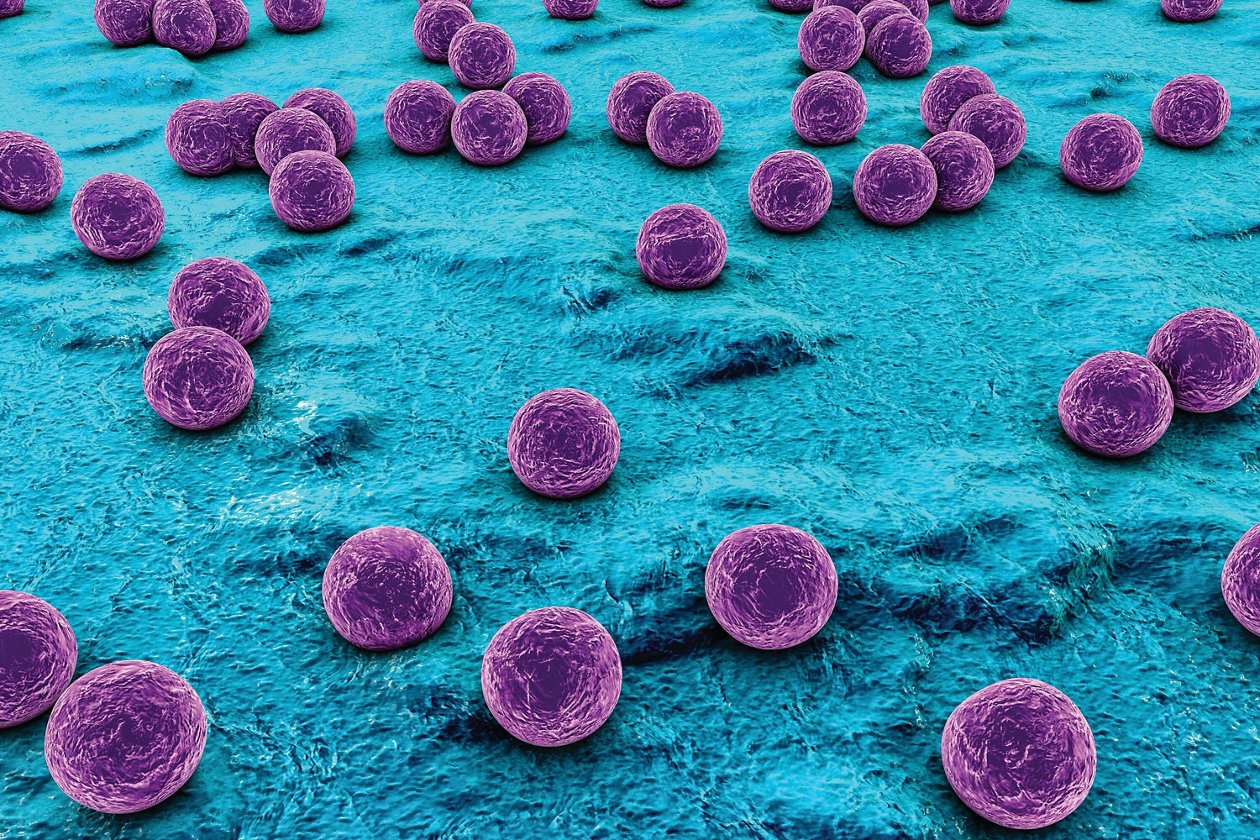
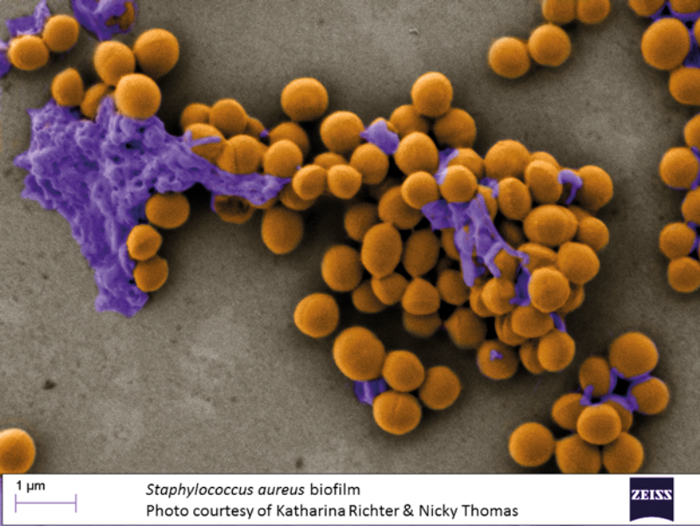
Staphylococcus spp. have been associated with cases of healthcare associated infections due to their high incidence in isolates from the hospital environment and their ability to cause infections in immunocompromised patients; synthesize biofilms on medical instruments, in the case of negative coagulase species; and change in genetic material, thus making it possible to disseminate genes that code for the acquisition of resistance mechanisms against the action of antibiotics. This study evaluated the presence of blaZ, femA, and mecA chromosomal and plasmid genes of Staphylococcus spp. using the qPCR technique. The results were associated with the phenotypic expression of resistance to oxacillin and penicillin G. We found that the chromosomal femA gene was present in a greater proportion in S. intermedius when compared with the other species analyzed, while the plasmid-borne mecA gene was prevalent in the S. aureus samples. The binary logistic regression performed to verify the association among the expression of the genes analyzed and the acquisition of resistance to oxacillin and penicillin G were not significant in any of the analyses, p > 0.05.
Water, Free Full-Text

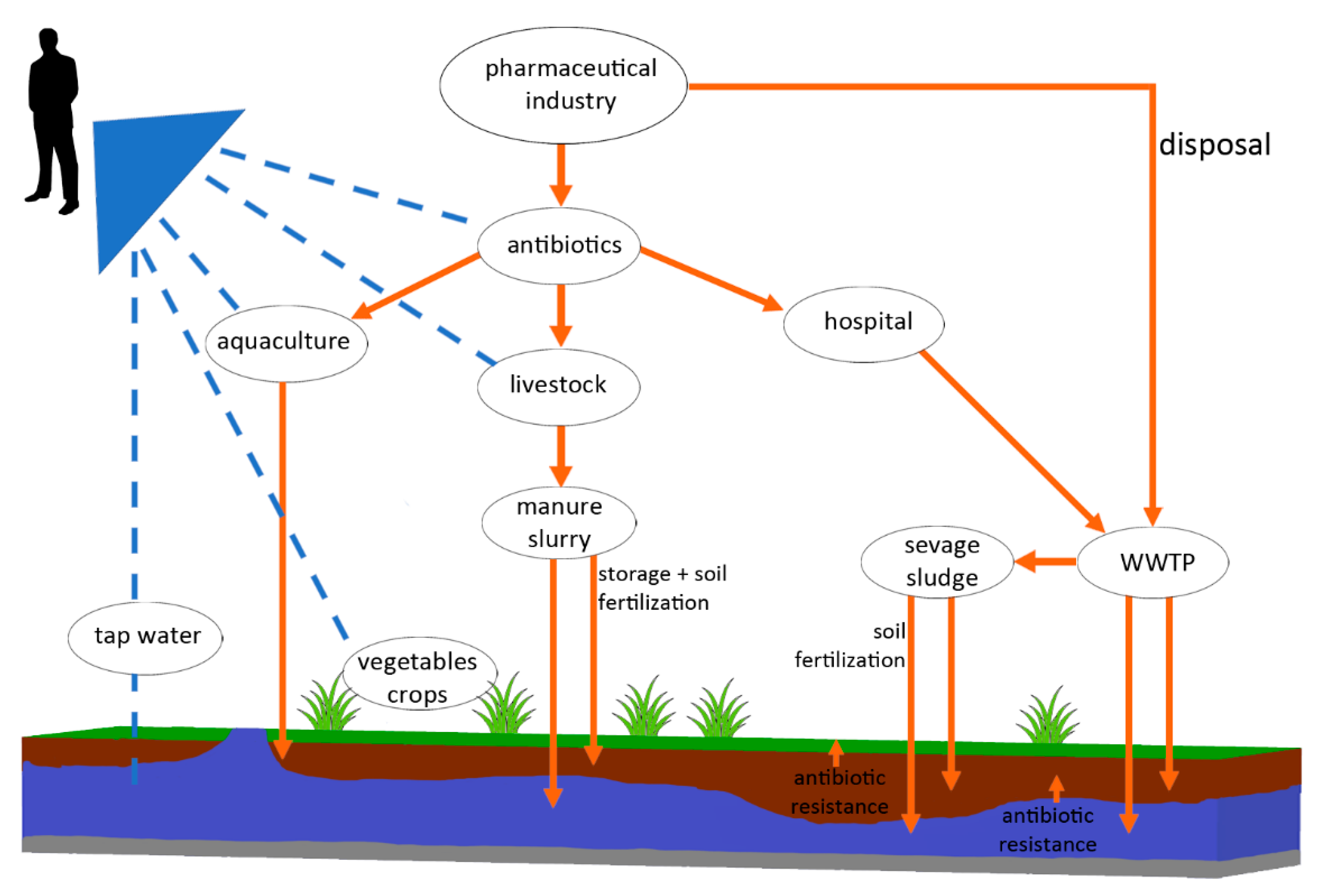
Active antibiotic resistome in soils unraveled by single-cell
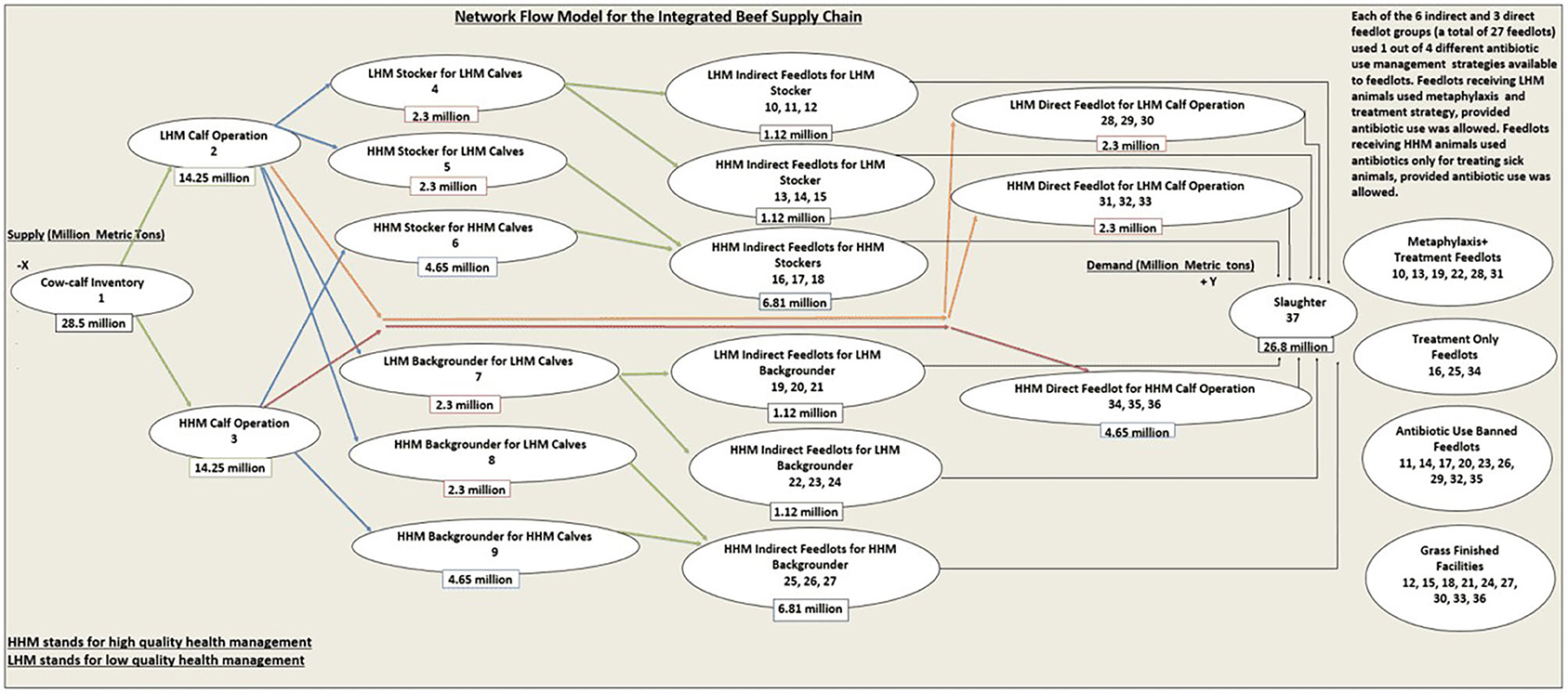
Frontiers System Economic Costs of Antibiotic Use Elimination in

Antibiotics: Nursing Pharmacology Study Guide

Alternatives to Conventional Antibiotics in the Era of
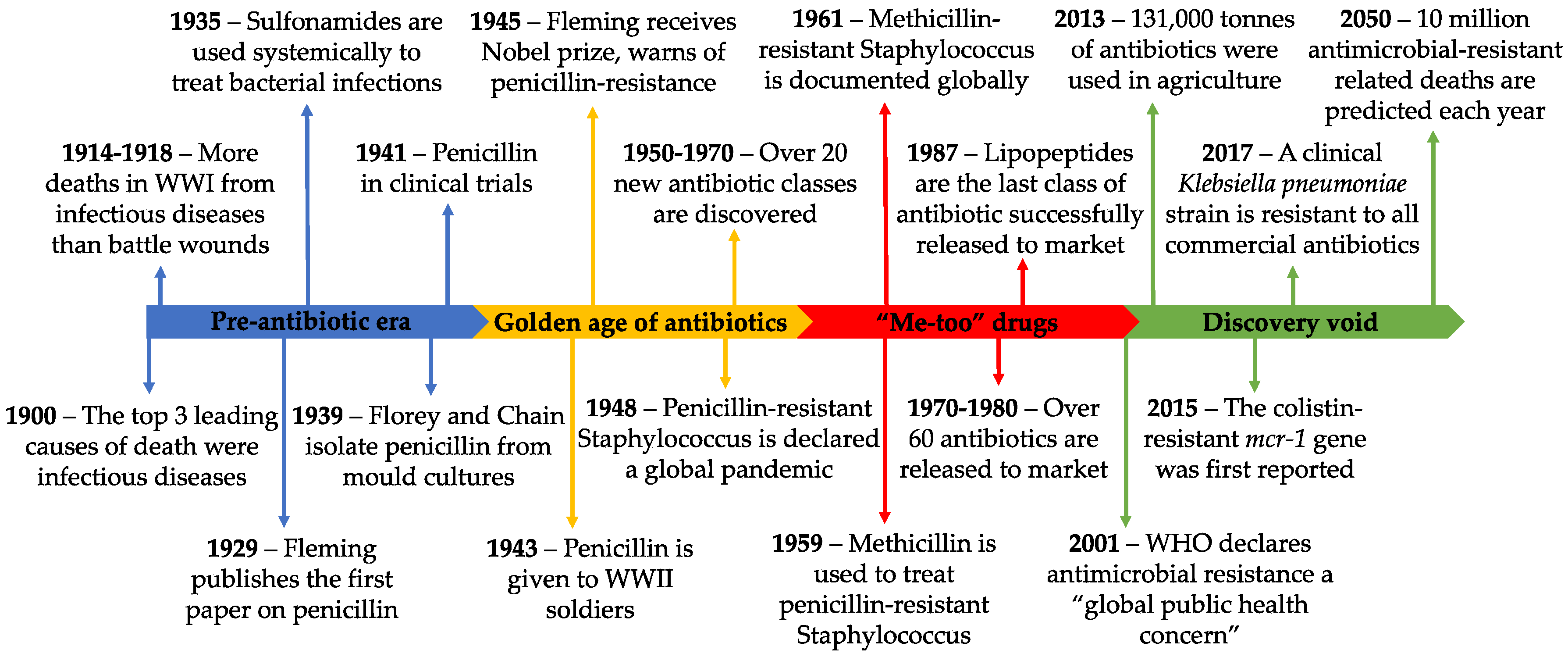
IJMS, Free Full-Text
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25163788/rbG0T_over_5_million_kilograms_of_antibiotics_were_sold_for_use_in_pork_and_beef_in_2022.png)
The meat industry's antibiotic drug problem, explained - Vox

Antibiotic-free poultry production: All you need to know

Toward a Comprehensive Strategy to Mitigate Dissemination of
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)