Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
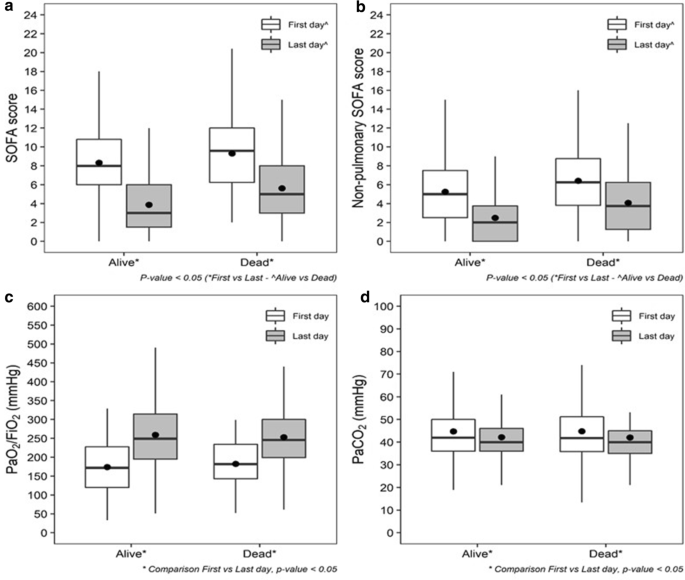
Beyond their role in hemostasis, platelets have emerged as key contributors in the immune response; accordingly, the occurrence of thrombocytopenia during sepsis/septic shock is a well-known risk factor of mortality and a marker of disease severity. Recently, some studies elucidated that the response of platelets to infections goes beyond a simple fall in platelets count; indeed, sepsis-induced thrombocytopenia can be associated with—or even anticipated by—several changes, including an altered morphological pattern, receptor expression and aggregation. Of note, alterations in platelet function and morphology can occur even with a normal platelet count and can modify, depending on the nature of the pathogen, the pattern of host response and the severity of the infection. The purpose of this review is to give an overview on the pathophysiological interaction between platelets and pathogens, as well as the clinical consequences of platelet dysregulation. Furthermore, we try to clarify how understanding the nature of platelet dysregulation may help to optimize the therapeutic approach.

Cell-free mutant analysis combined with structure prediction of a lasso peptide biosynthetic protein B2

Cell-free expression and synthesis of viruses and bacteriophages: applications to medicine and nanotechnology - ScienceDirect
Serial Number Alcohol 120 1.9 6 - Colaboratory

Nucleic acid biomarkers of immune response and cell and tissue damage in children with COVID-19 and MIS-C - ScienceDirect

The cell-free system: A new apparatus for affordable, sensitive, and portable healthcare - ScienceDirect

Cell-Free Protein Synthesis: Methods and Protocols

Postbiotics-parabiotics: the new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods, Microbial Cell Factories
Biology, Free Full-Text
Full-spectrum cell-free RAN for 6G systems: s
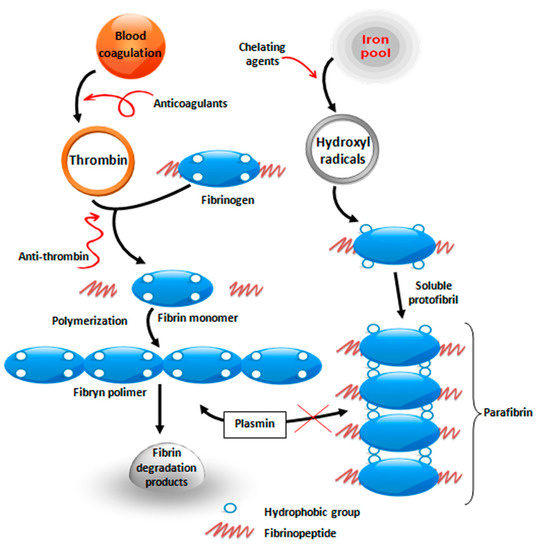
Polimer Program Get File - Colaboratory
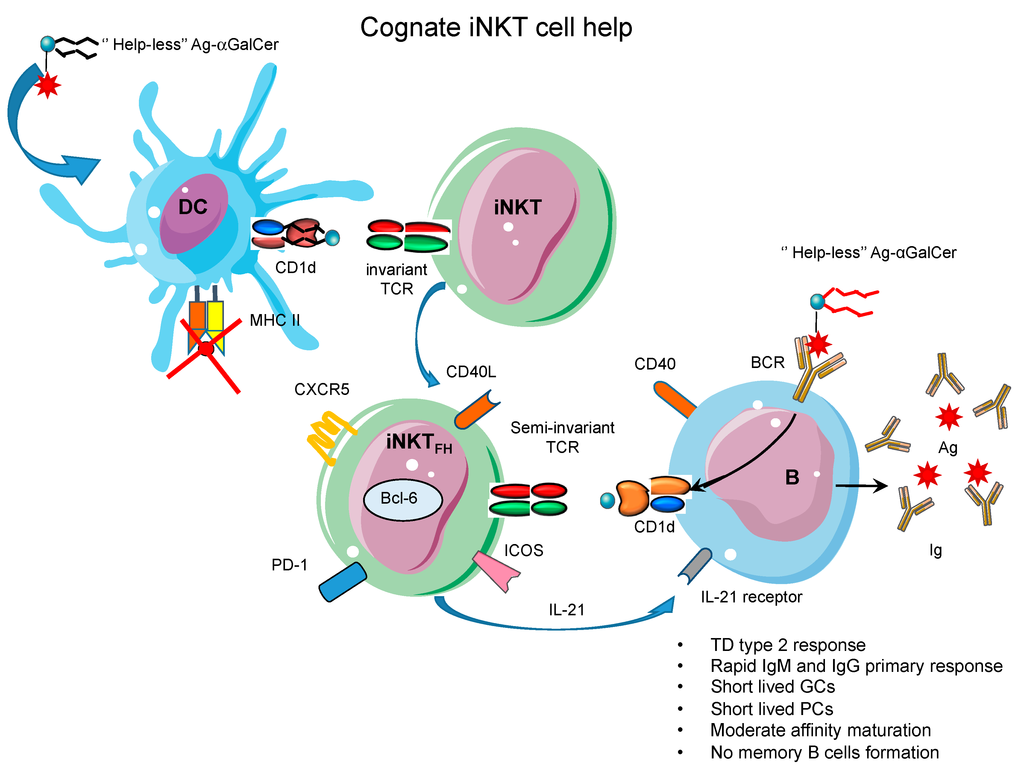
Antibodies, Free Full-Text
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)