Diseases, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
(1) Introduction: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of injury and mortality worldwide, carrying an estimated cost of $38 billion in the United States alone. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been investigated as a standardized biomarker that can be used to predict outcomes of TBI. The aim of this review was to determine the prognostic utility of NLR among patients admitted for TBI. (2) Methods: A literature search was conducted in PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science in November 2022 to retrieve articles regarding the use of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as a prognostic measure in traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients. Inclusion criteria included studies reporting outcomes of TBI patients with associated NLR values. Exclusion criteria were studies reporting only non-primary data, those insufficiently disaggregated to extract NLR data, and non-English or cadaveric studies. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale was utilized to assess for the presence of bias in included studies. (3) Results: Following the final study selection 19 articles were included for quantitative and qualitative analysis. The average age was 46.25 years. Of the 7750 patients, 73% were male. Average GCS at presentation was 10.51. There was no significant difference in the NLR between surgical vs. non-surgical cohorts (SMD 2.41 95% CI −1.82 to 6.63, p = 0.264). There was no significant difference in the NLR between bleeding vs. non-bleeding cohorts (SMD 4.84 95% CI −0.26 to 9.93, p = 0.0627). There was a significant increase in the NLR between favorable vs. non-favorable cohorts (SMD 1.31 95% CI 0.33 to 2.29, p = 0.0090). (4) Conclusions: Our study found that NLR was only significantly predictive for adverse outcomes in TBI patients and not surgical treatment or intracranial hemorrhage, making it nonetheless an affordable alternative for physicians to assess patient prognosis.

Data collections - WHO

MRI-Derived Myocardial Strain Measures in Normal Subjects

Management of Huanglongbing (HLB) by an Intensive Vector and Disease Control in the Surroundings of the Orchard, in Addition to Planting HLB-Free Trees in Okinawa, Japan
All CDs are intact, no scratches.

The Autoimmune Solution: Prevent and Reverse the Full Spectrum of Inflammatory Symptoms and Diseases

Neurofibromatosis 1 French national guidelines based on an extensive literature review since 1966, Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases

Diseases - Classification, Types and Causes of Diseases

Automatic classification of diseases from free-text death certificates for real-time surveillance – topic of research paper in Biological sciences. Download scholarly article PDF and read for free on CyberLeninka open science hub.
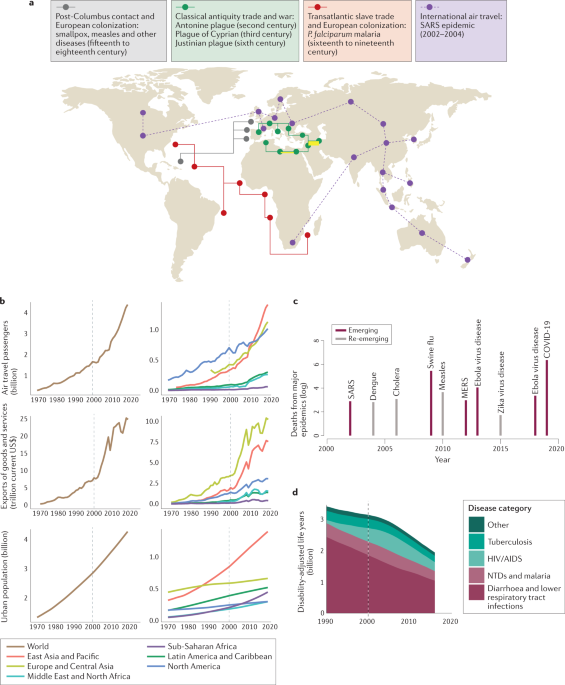
Infectious disease in an era of global change
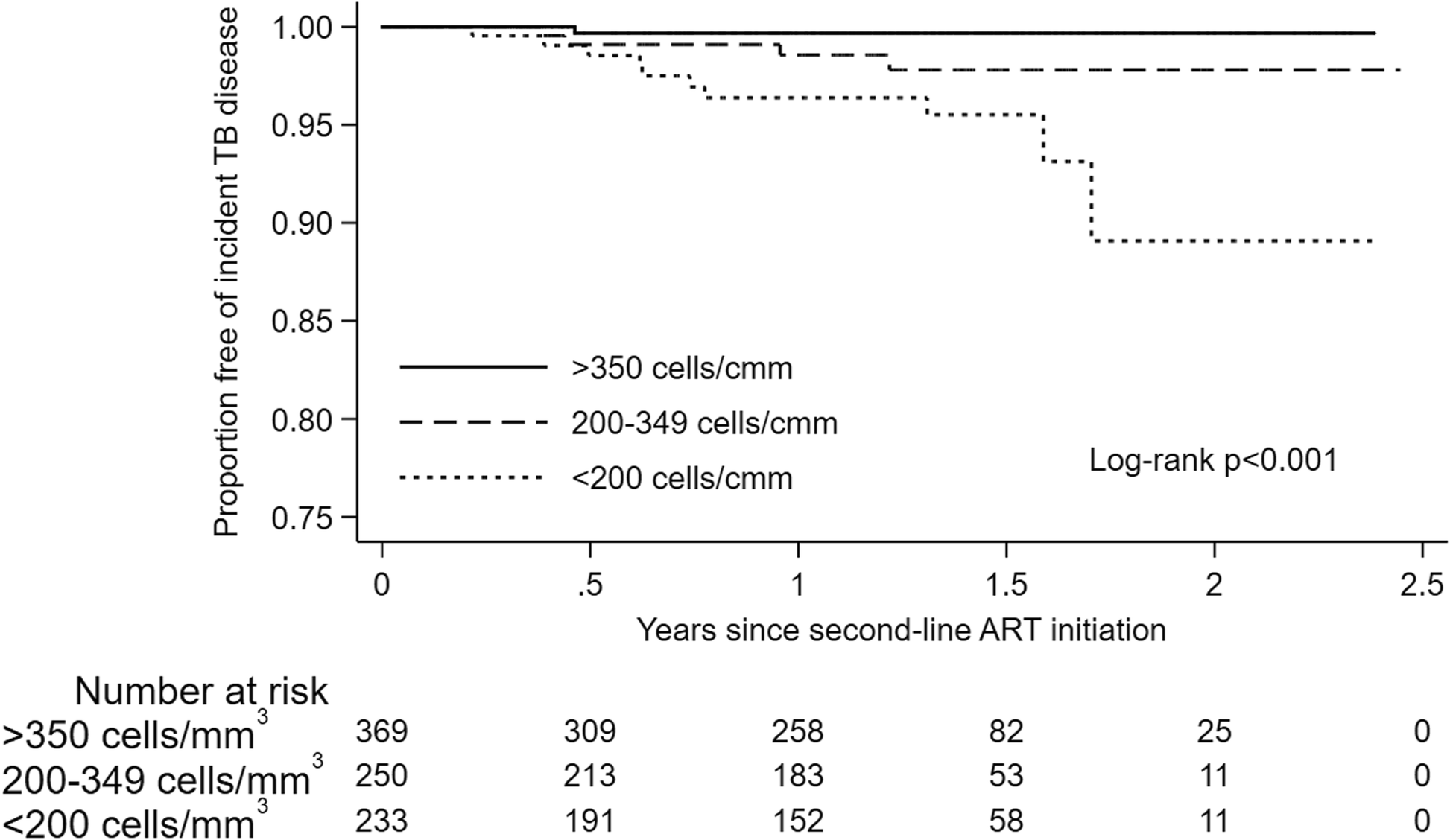
Incidence of tuberculosis in HIV-infected adults on first- and second-line antiretroviral therapy in India, BMC Infectious Diseases

IDSA GUIDELINES Bundle (free trial) - Coccidioidomycosis

Global Effect of Modifiable Risk Factors on Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)