Pathogens, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
In Brazil, blood donation is regulated by the Brazilian Ministry of Health, and all States follow the same protocol for clinical and laboratory screening. Brazil is an endemic country for Chagas disease (CD), caused by Trypanosoma cruzi, and for leishmaniasis, caused by a species of Leishmania spp. Screening for leishmaniosis is not routinely performed by blood banks. Given the antigenic similarity between T. cruzi and Leishmania spp., cross-reactions in serological tests can occur, and inconclusive results for CD have been found. The objective of this study was to apply molecular techniques, e.g., nPCR, PCR, and qPCR, to clarify cases of blood donation candidates with non-negative serology for CD and to analyze the difference between the melting temperature during real-time PCR using SYBR Green. Thirty-seven cases that showed non-negative results for CD using chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA) tests from blood banks in Campo Grande, MS, and Campinas, SP, were analyzed. In the serum samples, 35 samples were evaluated by ELISA, and 24.3% (9/35) showed positive results for CD. nPCR was able to detect 12 positive results in 35 samples (34.28%). qPCR for T. cruzi was quantifiable in the samples that showed a value ≥0.002 par eq/mL (parasite equivalents per milliliter), and in 35 samples, 11 (31.42%) were positive. Of all evaluated samples using the described tests (CMIA, ELISA, nPCR, and qPCR), 18 (48.6%) were positive for CD. For MCA by qPCR, the melting temperature was 82.06 °C ± 0.46 for T. cruzi and 81.9 °C ± 0.24 for Leishmania infantum. The Mann–Whitney test showed a significant value of p < 0.0001. However, the differentiation between T. cruzi and L. infantum could not be considered due to temperature overlap. For leishmaniasis, of the 35 samples with non-negative serology for CD tested by the indirect fluorescent antibody test (IFAT), only one sample (2.85%) was positive (1:80). The PCR for Leishmania spp. was performed on 36 blood samples from donation candidates, and all were negative. qPCR for L. infantum showed 37 negative results for the 37 analyzed samples. The data presented here show the importance of performing two different tests in CD screening at blood banks. Molecular tests should be used for confirmation, thereby improving the blood donation system.

Sequential Infection with Common Pathogens Promotes Human-like Immune Gene Expression and Altered Vaccine Response - ScienceDirect

The Disease Triangle: Fundamental Concept for Disease Management - Nursery and Flower Grower - ANR Blogs
Pathogen CK-12 Foundation
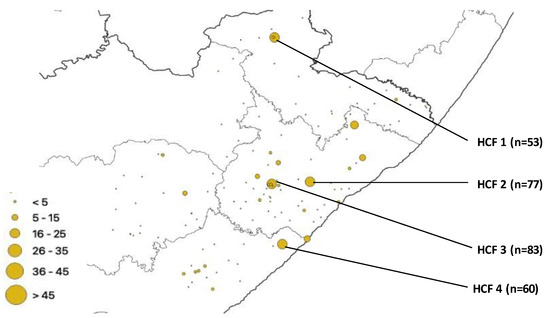
Hcf Practice Maps - Colaboratory

SOLUTION: Ati vocabulary full 2023 2024 - Studypool

Ecological and socioeconomic factors associated with the human burden of environmentally mediated pathogens: a global analysis - The Lancet Planetary Health

Programing of an Intravascular Immune Firewall by the Gut Microbiota Protects against Pathogen Dissemination during Infection - ScienceDirect
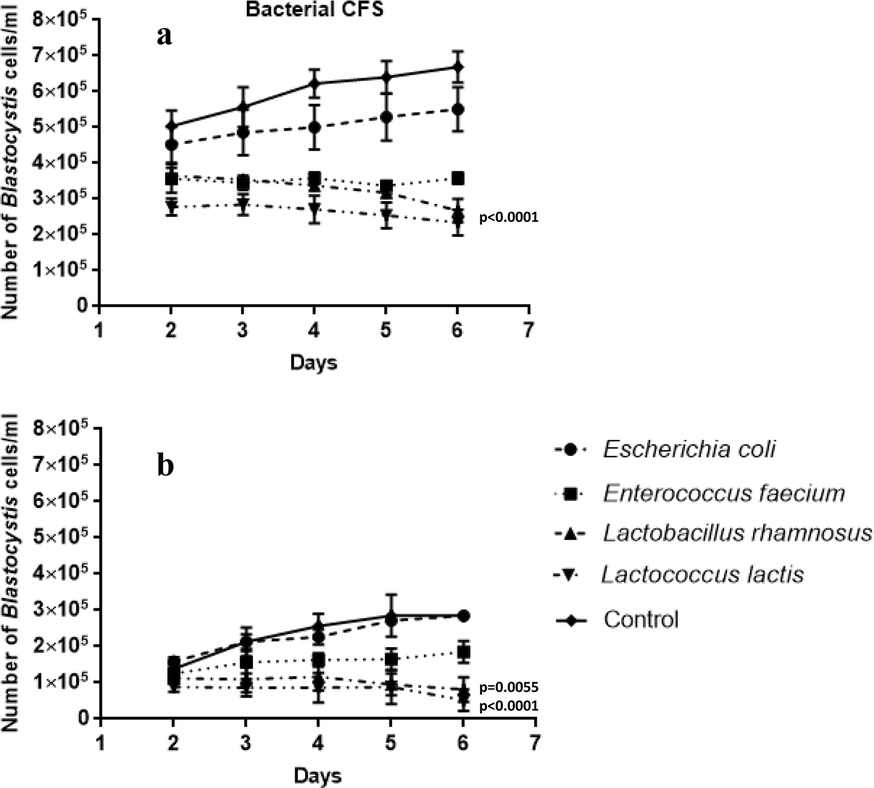
The influence of probiotic bacteria and human gut microorganisms causing opportunistic infections on Blastocystis ST3, Gut Pathogens
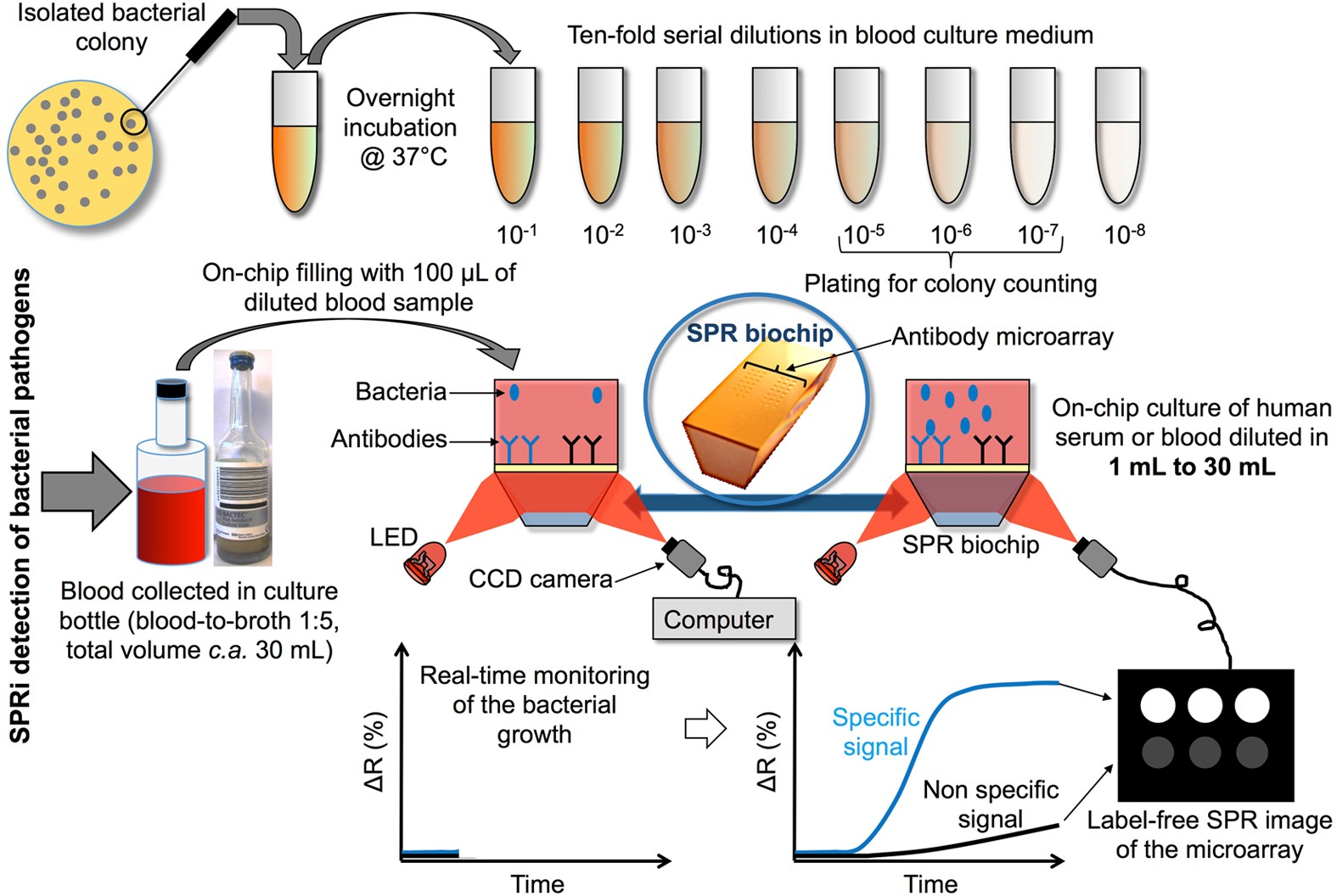
Biochips for Direct Detection and Identification of Bacteria in Blood Culture-Like Conditions
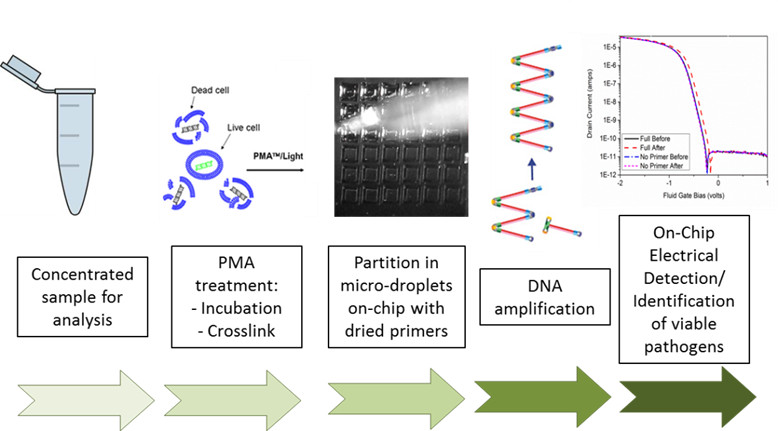
Detection of Viable Pathogens Using Label-Free Electrical Detection of Nucleic Acid Amplification : LIBNA
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)



:quality(75)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/elcomercio/75HUWSRZLFD53C5ZYPIL2Y434A.jpg)
