α-Synuclein Aggregation in Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Parkinson’s disease, the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide, is characterized by the accumulation of protein deposits in the dopaminergic neurons. These deposits are primarily composed of aggregated forms of α-Synuclein (α-Syn). PD is a complex pathology initially associated with motor deficiencies, as a result of an acute neuronal loss in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc), with a significant dopaminergic (DA) impairment.

Mechanism of Anti-α-Synuclein Immunotherapy

Intermediates of α-synuclein aggregation: Implications in Parkinson's disease pathogenesis - ScienceDirect

Current hypotheses for the involvement of a-synuclein in Parkinson's
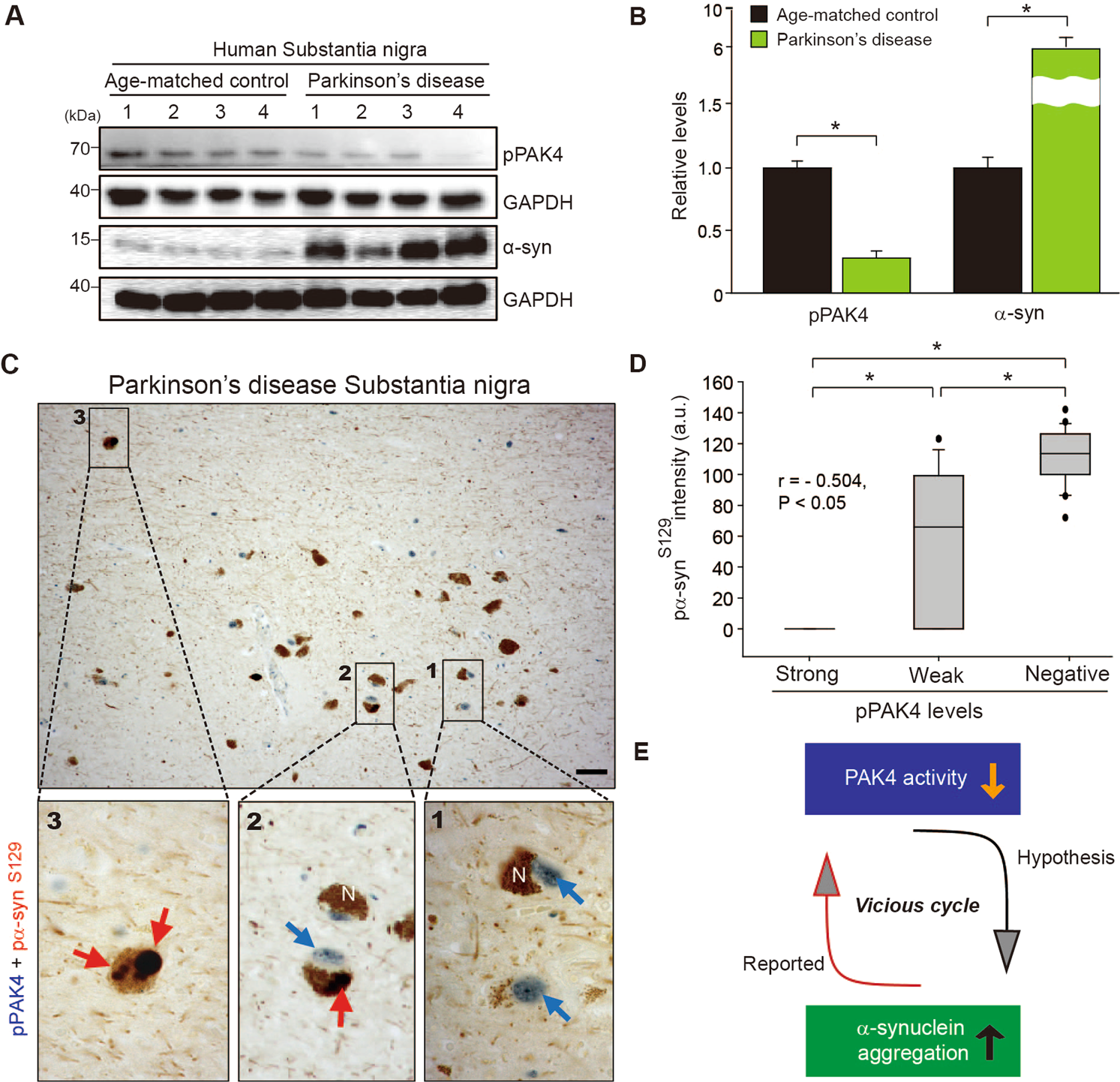
p21-activated kinase 4 controls the aggregation of α-synuclein by reducing the monomeric and aggregated forms of α-synuclein: involvement of the E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4-1
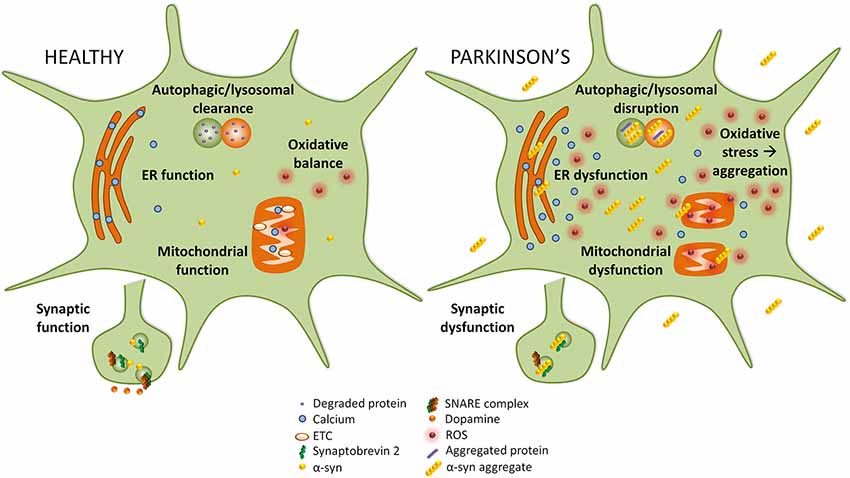
Frontiers Targeting Alpha-Synuclein as a Therapy for Parkinson's Disease
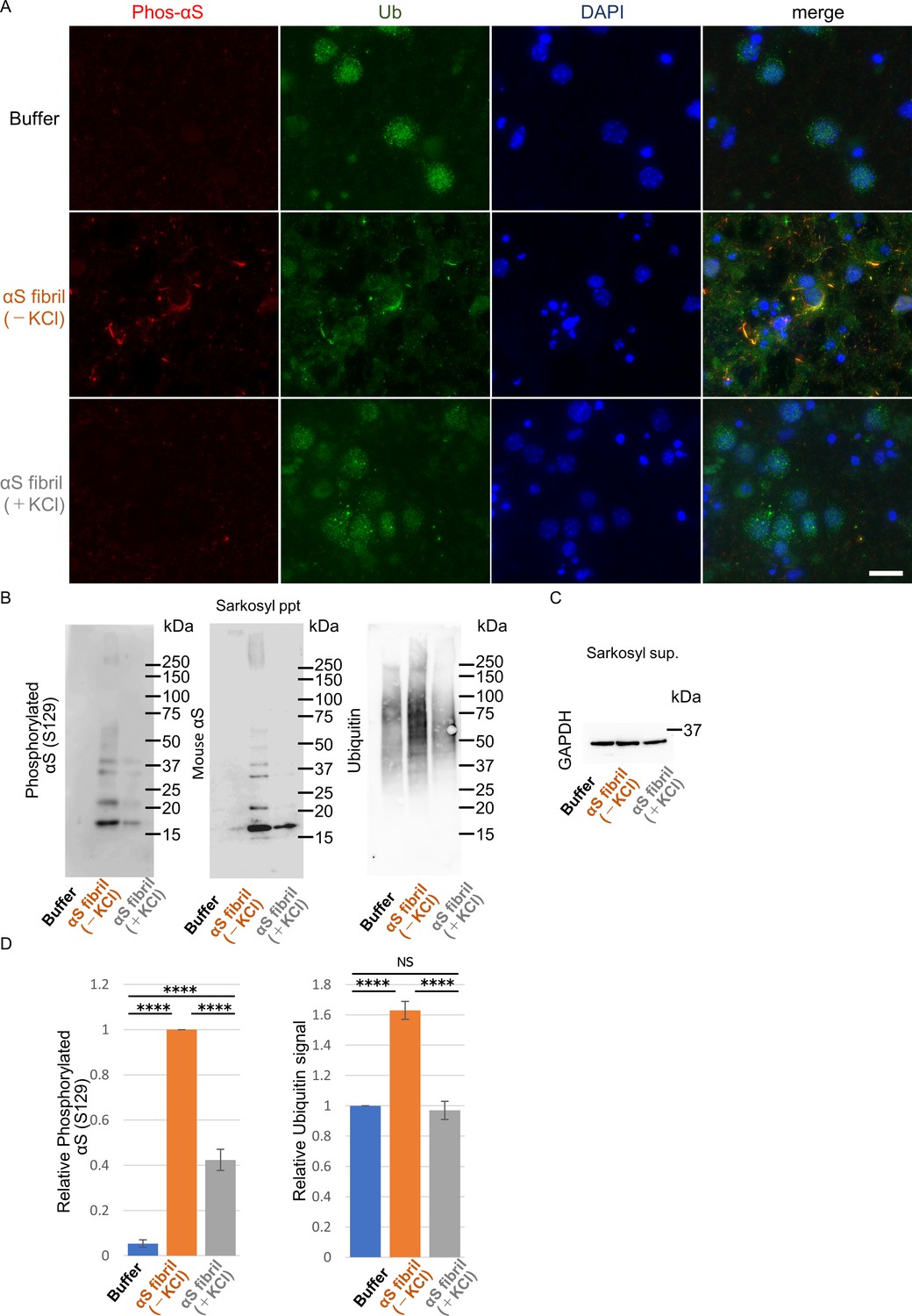
α-synuclein strains that cause distinct pathologies differentially inhibit proteasome

Tuning the Balance between Fibrillation and Oligomerization of α-Synuclein in the Presence of Dopamine

ISIS Studying the influence of salts on α-synuclein aggregation, a hallmark of Parkinson's disease

Active alpha-synuclein proteins
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)