Antibody and CD8+ T Cell Responses: How the Delta Variant Evades Immunity?
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
SARS-CoV-2 vaccines have reduced efficiency against variants of concern. Find out how antibody and T cell responses are affected by variant associated mutations.

Emergence of immune escape at dominant SARS-CoV-2 killer T cell epitope - ScienceDirect
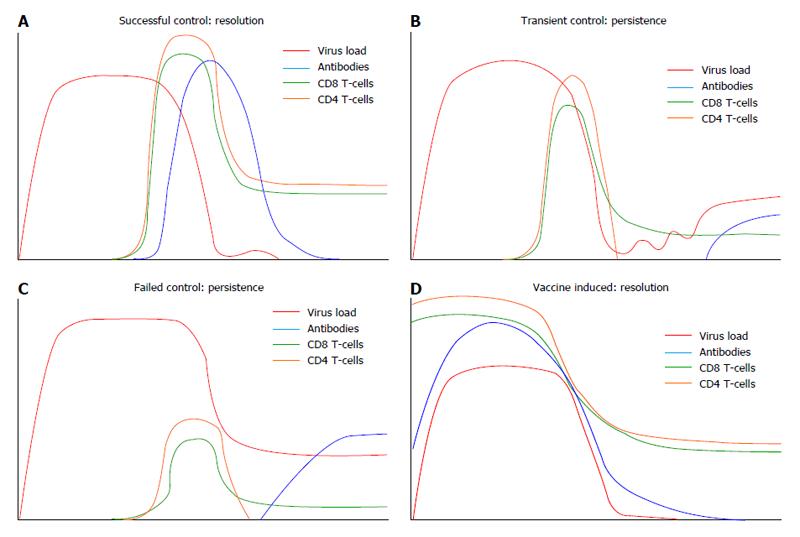
Immune mechanisms of vaccine induced protection against chronic hepatitis C virus infection in chimpanzees
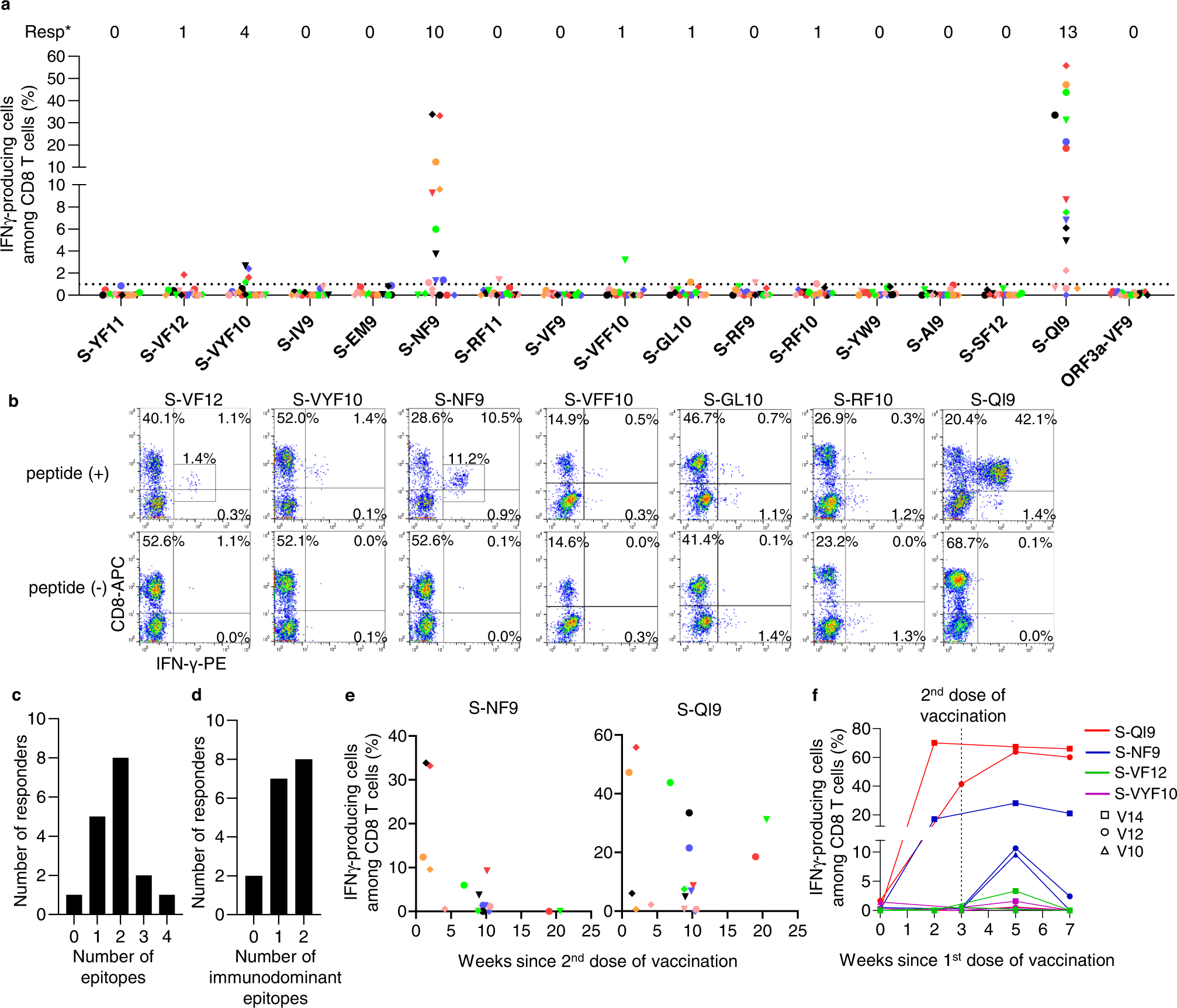
Long-term memory CD8+ T cells specific for SARS-CoV-2 in individuals who received the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine
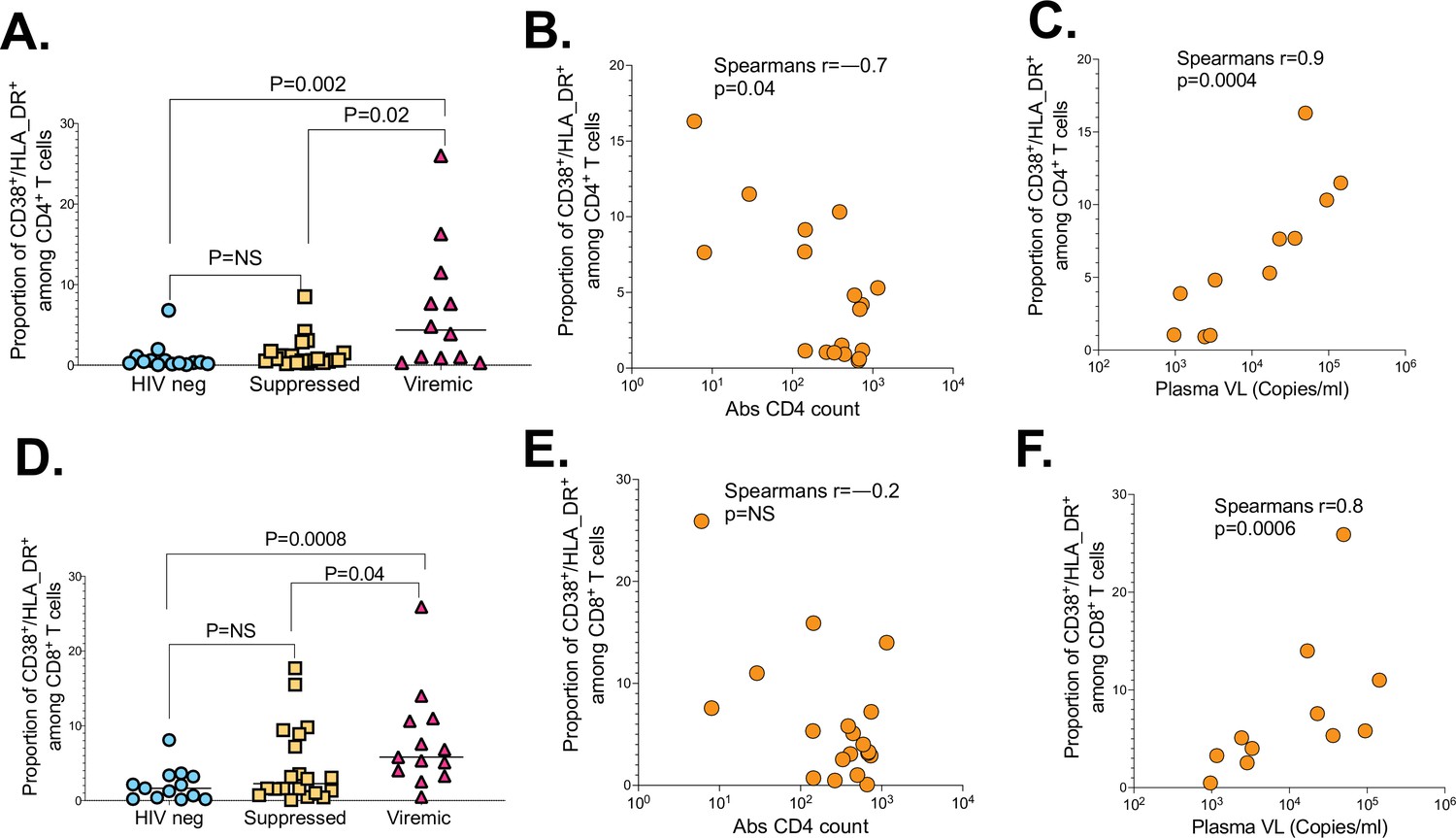
Unsuppressed HIV infection impairs T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection and abrogates T cell cross-recognition

T cell responses to the ancestral, Beta, Delta and Omicron SARS-CoV-2

Prior vaccination enhances immune responses during SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infection with early activation of memory T cells followed by production of potent neutralizing antibodies

Divergent SARS-CoV-2 Omicron–reactive T and B cell responses in COVID-19 vaccine recipients
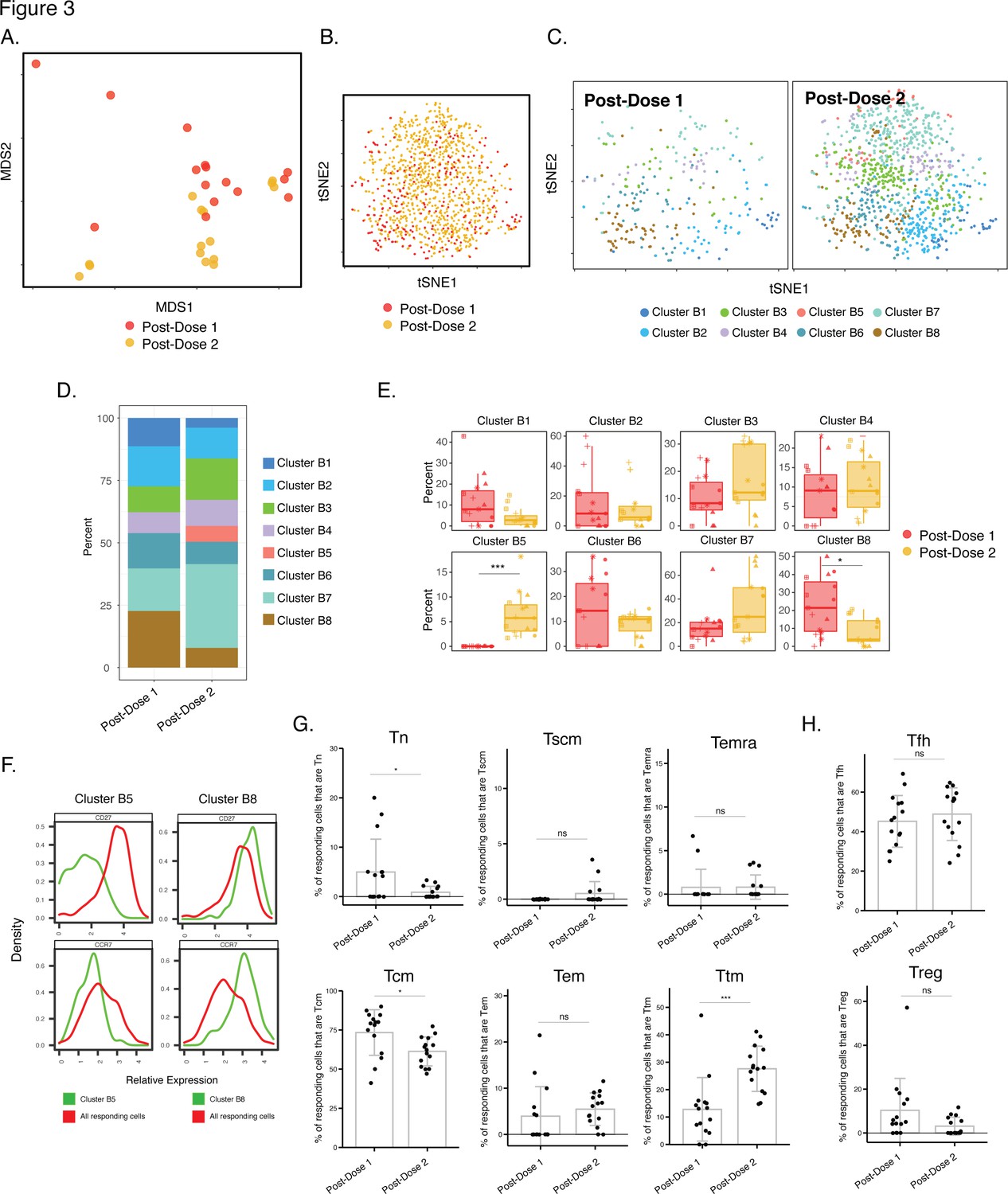
mRNA vaccine-induced T cells respond identically to SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern but differ in longevity and homing properties depending on prior infection status

SARS-CoV-2 mutations in MHC-I-restricted epitopes evade CD8+ T cell responses
Op-Ed: Could the COVID-19 virus mutate to evade the vaccines? - Los Angeles Times
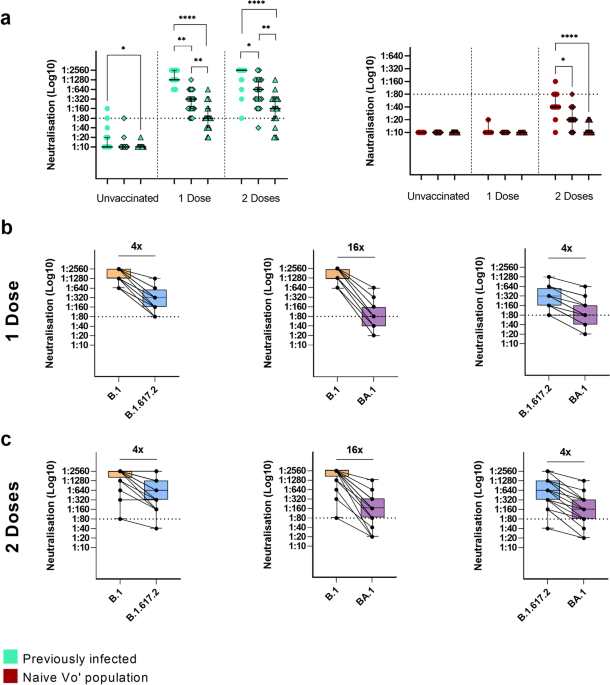
Neutralising reactivity against SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants by vaccination and infection history, Genome Medicine

Immunity in Omicron SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough COVID-19 in vaccinated adults
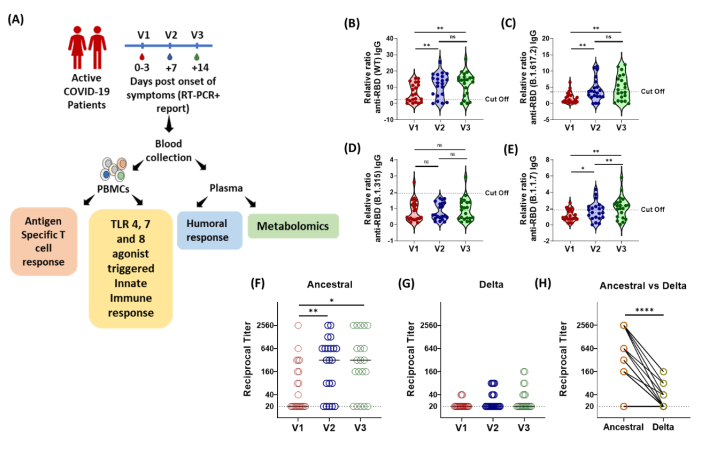
COVID-19: antigen-specific T cell response and immuno-metabolomic signatures
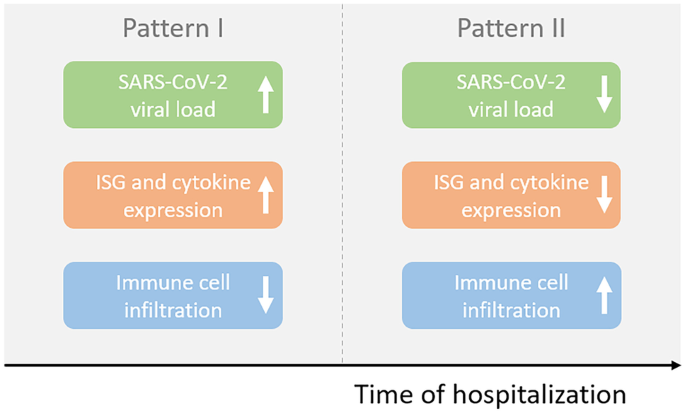
Role of T cells in severe COVID-19 disease, protection, and long term immunity

Targeting Multiple Conserved T-Cell Epitopes for Protection against COVID-19 Moderate-Severe Disease by a Pan-Sarbecovirus Vaccine
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)