Site-specific phosphorylations of the Arf activator GBF1 differentially regulate GBF1 function in Golgi homeostasis and secretion versus cytokinesis
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

ARF family G proteins and their regulators: roles in membrane transport, development and disease
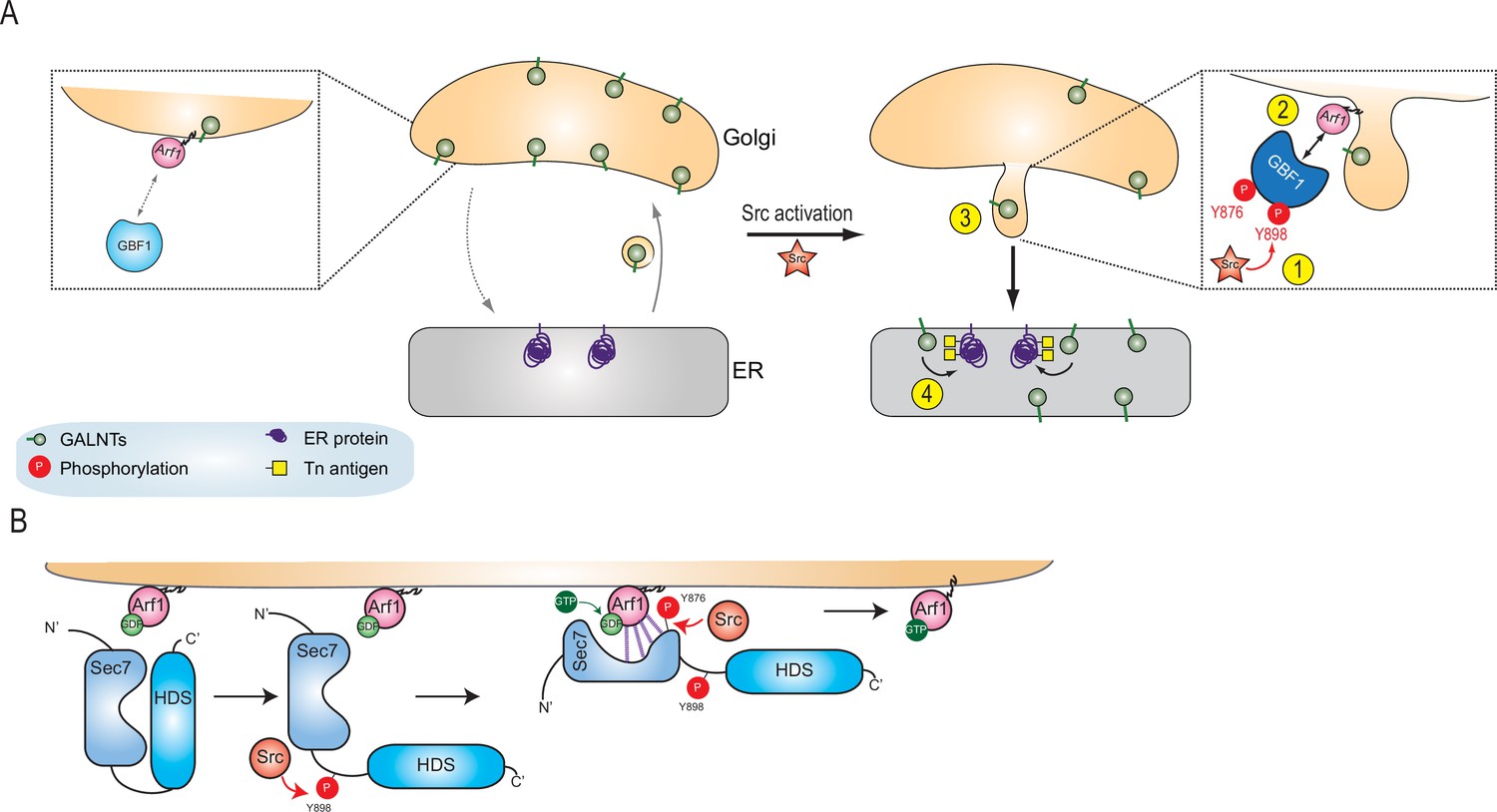
Src activates retrograde membrane traffic through phosphorylation of GBF1

Site-specific phosphorylations of the Arf activator GBF1 differentially regulate GBF1 function in Golgi homeostasis and secretion versus cytokinesis

PDF) Inheritance of the Golgi Apparatus and Cytokinesis Are Controlled by Degradation of GBF1

Localization of Large ADP-Ribosylation Factor-Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors to Different Golgi Compartments: Evidence for Distinct Functions in Protein Traffic

Localization of Large ADP-Ribosylation Factor-Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors to Different Golgi Compartments: Evidence for Distinct Functions in Protein Traffic

Regulators and Effectors of Arf GTPases in Neutrophils. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Model of how GBF1, Arf1, Miro2 and dynein may regulate mitochondrial
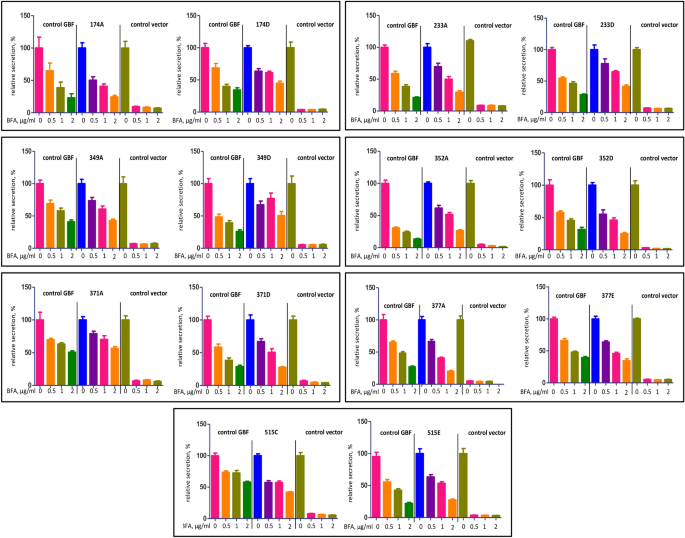
Site-specific phosphorylations of the Arf activator GBF1 differentially regulate GBF1 function in Golgi homeostasis and secretion versus cytokinesis
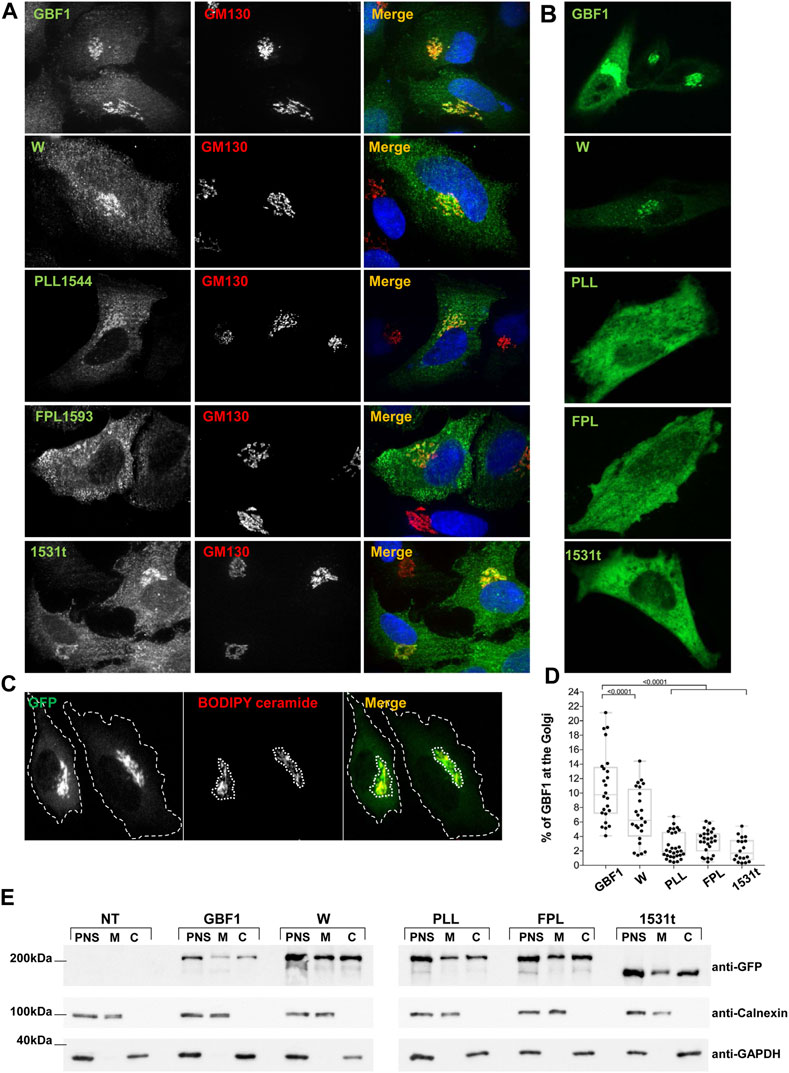
Frontiers The Arf-GEF GBF1 undergoes multi-domain structural shifts to activate Arf at the Golgi
The GBF1 Sec7 domain directly interacts with the ATGL (300-504) domain
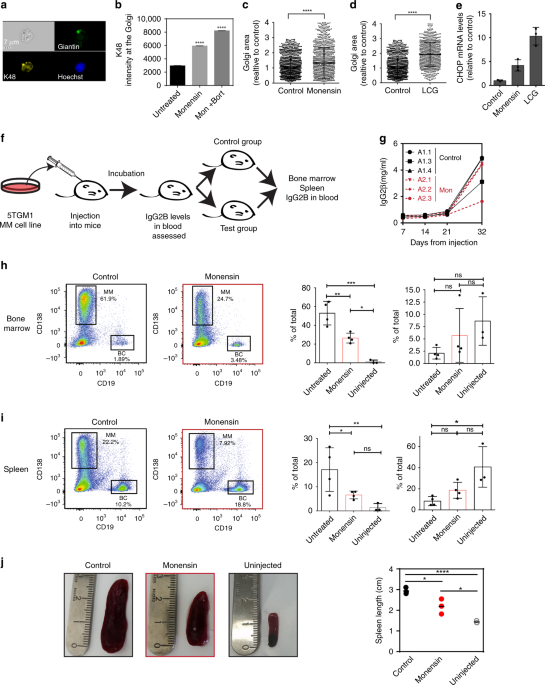
Golgi organization is regulated by proteasomal degradation

Miro GTPases interact physically with GBF1. (A,B) RPE1 cells were
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)